Sineimage ColorChecker Color Rendition Test Chart
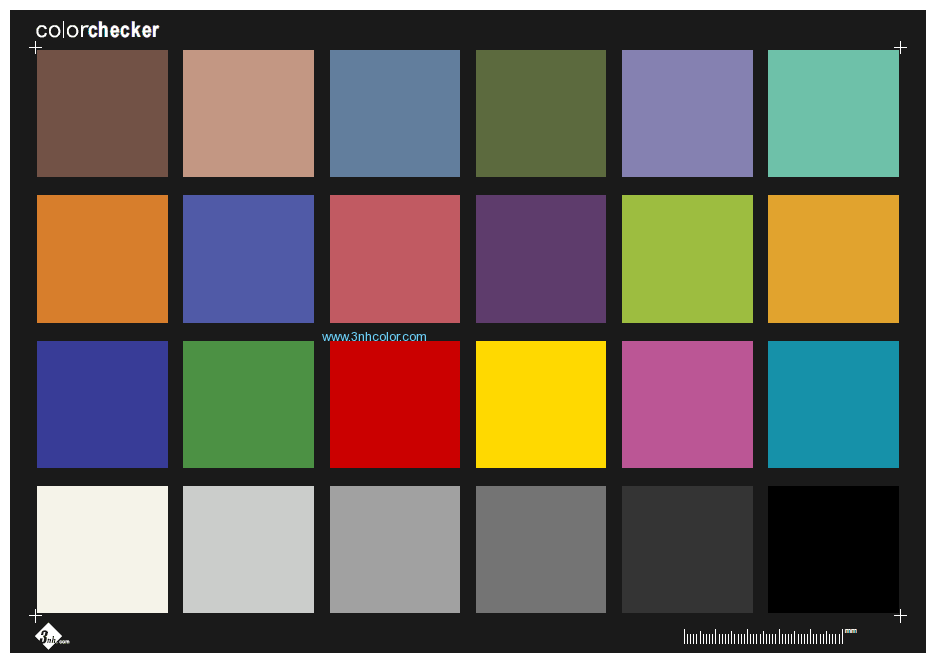
Sineimage ColorChecker Color Rendition Test Chart consists of a 6-step gray scale, plus three primary colors (red, green, blue), subtractive three primary colors (yellow, product, green), as well as skin color and the real color of simulated natural objects. This test chart has 24 pure color blocks, from left to right and from top to bottom, marked 1-24 respectively. So it's also called 24 color card. For camera color and white balance test, we use the colorchecker test chart in different environments to shoot and compare under the corresponding white balance mode. We can observe the restoration of various types of color, and also observe the accuracy of their white balance.
ColorChecker Test Chart Applications
Digital cameras: check the color restoration of cameras, lenses and optical systems, correct the image color of digital cameras, compare and test the target white balance, and reproduce the true color in the color restoration system.
Video image: check the quality of static and dynamic color reproduction of the camera, check the color restoration of the camera and its optical system and the color restoration of the projection system, etc.
Electronic industry: detection scanner, display, monitor color restoration.
Printing industry: detection of any printing and proofing procedures, detection of film, light, filters and paper.
Use of ColorChecker Test Chart
(1) color restoration
The Colorchecker test chart can restore the true color under any illumination. The first thing you want to shoot is the ColorChecker standard color card. The specific steps are as follows:
1. Put the ColorChecker test chart on the scene (no need to fill the viewfinder)
2. Ensure that the camera can capture all the color blocks.
3. Let the ColorChecker test chart be located in the representative part of the composition, not in the shadows or in the highlights where the exposure is excessive.
4. Don't let the light reflected by other objects project onto the color card.
5. Take photos with color cards
6. When opened in Photoshop, there will be a built-in reference point
7. Sampling black blocks with a color sampler. The difference between RGB should be within 7 units, about 245
8. Sampling white blocks. RGB is about 245
9. Check the color deviation. Choose the middle gray color block, RGB value is about 128, the difference between each other should not exceed 7.
10. If the reading scores deviate, use the horizontal or curve to return to the above state.
11. Save the settings. This setting can be used for other graphics under the same illumination conditions.
12. Further visual color matching can be done with other color blocks.
Note: Corrected displays should be used, and physical ColorChecker test cards should be placed under standard light sources with controlled lighting conditions.

